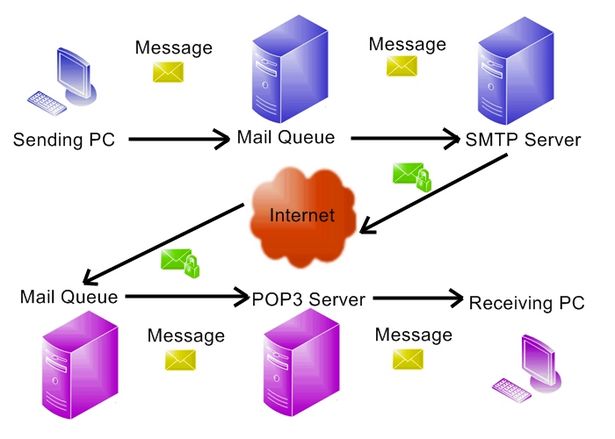
The ability to provide E-mail services to clients includes two critical functions: SMTP and POP3. Most e-mail systems that send mail over the Internet use SMTP to send messages from one server to another; the messages can then be retrieved with an e-mail client using either POP or IMAP. In addition, SMTP is generally used to send messages from a mail client to a mail server.And POP3 is used to receive the messages from mail client. This is why you need to specify both the POP or IMAP server and the SMTP server when you configure your e-mail application.
The ability to provide E-mail services to clients includes two critical functions: SMTP and POP3. Most e-mail systems that send mail over the Internet use SMTP to send messages from one server to another; the messages can then be retrieved with an e-mail client using either POP or IMAP. In addition, SMTP is generally used to send messages from a mail client to a mail server.And POP3 is used to receive the messages from mail client. This is why you need to specify both the POP or IMAP server and the SMTP server when you configure your e-mail application.
OUTGOING MAIL SERVER
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. When someone speaks of a SMTP server they are referring to an outgoing mail server. Most hosting companies do not offer access to SMTP servers. Because its difficult to maintain and defend and the want to cut corners with their customers.
SMTP service is the side of e-mail that allows clients to send outgoing e-mail messages to any valid e-mail address. The SMTP server performs two basic but important functions. First, it verifies that anyone attempting to send outgoing e-mail through the SMTP server has the right to do so. Secondly, it sends the outgoing mail and if undeliverable, sends the message back to the sender.
You need to configure your e-mail client so that it knows what SMTP server to use for sending outgoing e-mail messages. In order to send mail through the proper SMTP server, configure your e-mail client to access the SMTP Server: yourdomain.com or IP address.
INCOMING MAIL SERVER
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol (version 3), comprised of mailboxes for email systems. So that a user can retrieve email from a central location where the email is stored. POP3 accounts allow users to have mailboxes on a server with their domain name. This means that if you own the domain name yourdomain.com you can receive and send email at yourname @yourdomain.com.Post Office Protocol Version 3 provides a simple, standardized way for users to access mailboxes and download messages to their computers.
Most e-mail applications also known as an e-mail clients use the POP protocol, although some can use the newer IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol). In order to set up POP3 email accounts for your domain, your domain must be hosted on server which has nameservers.
Since POP3 allows a client computer to retrieve electronic mail from a POP3 server via a (temporary) TCP/IP or other connection, it does not provide for sending mail, which is assumed to be done via SMTP or some other method. POP is useful for computers, e.g. mobile or home computers, without a permanent network connection which therefore require a “post office” (the POP server) to hold their mail until they can retrieve it.
ADVANTAGE AND DISADVANTAGES OF POP3
POP3 email accounts require a piece of software called an email reader in order to send and receive email. Common applications that serve as email readers are: Netscape Messenger, Outlook Express, Outlook and Eudora etc.
POP3 or the Post Office Protocol is the oldest and best known of the two Internet message access protocols. It was designed to support “offline”/local email processing. Email is delivered to an email server. And a remote email client periodically downloads messages from this server to the user’s PC. Once the messages are delivered to the client they are permanently deleted from the email server.
One of the advantages of POP3 is that once the messages are delivered to the client PC the messages can be read whether connected to the Internet or not. It is a very popular email protocol and just about all email clients support it.
A disadvantage of the POP3 protocol is that it is inadequate for the mobile user. Since messages are permanently downloaded, the user will only be able to access the messages from one PC. A couple ways around this are mobile PCs (laptops, palmtops, etc.). Some email programs have an option to “leave the messages on the server “. The best way to work around this problem is to use IMAP.