If you are just beginning the process of finding a host for your website, you’ll probably be going through a steep learning curve when it comes to understanding all the jargon you need to know. To make things easier, we’ve put together a glossary of important website hosting tips that we think every website owner needs to know. We hope you find them useful.

-
Web Host
A web host, such as 4hostings, is a company that provides customers with the resources they need to broadcast their website over the internet. They provide the servers and software needed to achieve this and rent out space on those servers where clients can store their website files.
Web hosts also maintain their servers, keeping them up to date, optimized for best performance and secure from hackers and viruses. In addition, they also provide a range of other essential services, such as email hosting and backups.
-
Server
A server is a computer that is set up to deliver web pages to people’s browsers. It does this by using HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to send the files needed to form a web page when someone clicks on a link or types an address in a browser. When you run a website, the files you use to create it are stored on a server so they can be accessed over the internet.
-
Linux Server
A Linux server is one which runs on Linux operating system software. Linux is the most common OS used on servers and most websites will be run on Linux servers. One of the reasons for its popularity is because Linux is compatible with many apps needed to run websites.
-
Windows Server
A Windows server runs on a Microsoft Windows operating system. Websites may need to use this type of server if they want to utilize some of the features of Windows. However, this means they might be restricted in some of the other website software they use too. Windows servers tend to be more expensive than Linux ones.
-
Shared hosting
Shared hosting is the most affordable hosting solution available to website owners and is ideal for small websites and personal blogs. It is called shared hosting because many different user accounts are hosted on the hard drive of one physical server and they share all the resources of that server, e.g., memory, CPU and bandwidth.
-
VPS hosting
The next step up from shared hosting, a VPS or Virtual Private Server is a single physical server on which several smaller, virtual servers have been created. Whilst you still share the underlying hardware with other users, your VPS is totally independent of the other VPS on the server. This means you have more resources at your disposal and much greater freedom over the software you can install and how you configure your virtual server.
-
Dedicated server hosting
When you purchase dedicated server hosting, you have an entire server for your own requirements and can install and run any application you need to run your business. You also have some choice over the hardware specification you need and how it is configured. Dedicated servers have very large storage space and offer massive resources. This makes them expensive to run. However, only those who run very big and busy websites will need a dedicated server.
-
Cloud hosting
Cloud hosting is where you run your website from the cloud. In other words, it is hosted on a virtual server which is housed on a network of physical servers rather than on a single physical or virtual server. Cloud hosting, like dedicated hosting, is best for bigger websites. It is especially helpful for those websites that have to cope with large fluctuations in traffic and need capacity to scale up and scale down the resources they need. Cloud lets website owners do this affordably by offering a pay as you go pricing option for using extended resources.
-
Domain name
A domain name is what most people refer to as the website name. 4hostings’s domain name is 4hostings.com. Domain names are a combination of two elements: the actual name ‘4hostings’ and the extension, ‘.com’. Provided the name you want has not already been registered, you can use virtually any name you wish (there are some exceptions).
As for extensions, there is now a wide range to choose from. These are used to help categories your website. For example, .com refers to a commercial business, .org is used by non-profit organizations, .edu is for education establishments, etc. You should choose the one that is most appropriate for your website.
-
URL
URL, which stands for ‘uniform resource locator’, is essentially a web address. This is what you click on or type into a search engine to open a web page in your browser. Each page, post and image on your website has its own URL. For example, our homepage address is https://www.4hostings.com/, our blog address is http://blog.4hostings.com/
- IP address
Besides having a URL address, all websites have an IP (Internet Protocol) address. This is a unique number (e.g. 91.103.208.163) that is assigned to a device on a network. A URL cannot be understood by a computer, so when someone types one in a browser, it points to an IP address that computers can understand.
-
Domain name server (DNS)
DNS is the abbreviation for ‘domain name servers’. It is the link between the URL and the IP address. When you click on or type in a URL, the DNS finds the server that hosts the website you are searching for so it can be displayed in your browser.
When you create your website, you will need to register your domain name. It makes things much easier if your domain registrar and your web host are the same company. However, it is possible to have them as separate entities.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you’ll find these twelve definitions useful in helping you understand some of the more technical aspects of setting up your website and choosing a web host.
If you are considering setting up a website and are looking for an affordable web hosting plan that comes with a range of useful features and 24/7 technical support, check out our range of hosting.


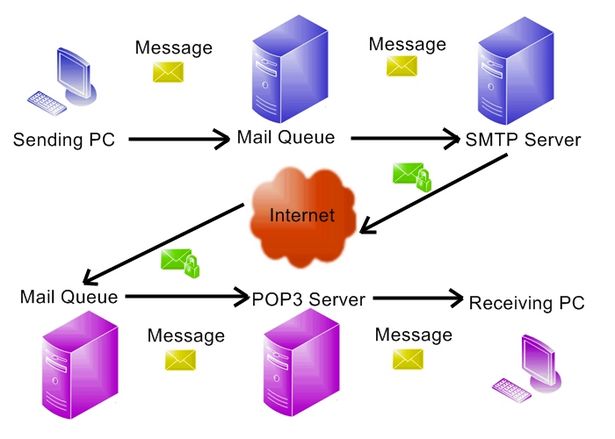
 The ability to provide E-mail services to clients includes two critical functions: SMTP and POP3. Most e-mail systems that send mail over the Internet use SMTP to send messages from one server to another; the messages can then be retrieved with an e-mail client using either POP or IMAP. In addition, SMTP is generally used to send messages from a mail client to a mail server.And POP3 is used to receive the messages from mail client. This is why you need to specify both the POP or IMAP server and the SMTP server when you configure your e-mail application.
The ability to provide E-mail services to clients includes two critical functions: SMTP and POP3. Most e-mail systems that send mail over the Internet use SMTP to send messages from one server to another; the messages can then be retrieved with an e-mail client using either POP or IMAP. In addition, SMTP is generally used to send messages from a mail client to a mail server.And POP3 is used to receive the messages from mail client. This is why you need to specify both the POP or IMAP server and the SMTP server when you configure your e-mail application.